|
|
hai 5 meses | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| Image | hai 5 meses | |
| README.md | hai 5 meses | |
README.md
JPS
Jump Point Search
参考文档: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/500807732 参考代码: https://github.com/ai-winter/ros_motion_planning/blob/master/src/core/path_planner/path_planner/src/graph_planner/jps_planner.cpp
概念解释
强制邻居
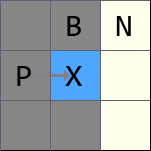
从 P 点进入 X 点,当前在 X 点
P 点可以通过 B 点 到达 N 点;P 点可以通过 X 点到达 N 点
如果此时 B 点变成障碍物,无法达到,那么 P 点到达 N 点只能通过 X 点
所以说 N 点是 X 点的强制邻居
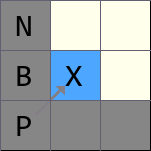
上图同理,如果 B 点为障碍物,那么 N 点只能通过 X 点才能到达
代码分析
基本结构定义
定义基本结构体 Node
class JNode : public Node
{
public:
/* @brief Construct a new JNode object
* @param x 节点对应 X 轴坐标
* @param y 节点对应 Y 轴坐标
* @param g 节点对应 到 StartNode 的 Cast
* @param h 节点对应 到 EndNode 的 Cast
* @param id 节点对应 的 ID
* @param pid 节点对应 的 Parent 的 ID
* @param fid 节点对应 强制邻居 Forced neighbor ID
*/
JNode(int x = 0, int y = 0, double g = 0.0, double h = 0.0, int id = 0, int pid = -1, int fid = 0)
: Node(x, y, g, h, id, pid), fid_(fid)
{}
struct compare_cost
{
bool operator()(const Node& n1, const Node& n2) const
{
return (n1.g() + n1.h() > n2.g() + n2.h()) || ((n1.g() + n1.h() == n2.g() + n2.h()) && (n1.h() > n2.h()));
};
};
}
- 定义 x 轴的长度为 nx_
- 定义 y 轴的长度为 ny_
定义 左 是 x 轴正方向;定义 上 是 y 轴正方向
// [left, right, top, bottom, left-top, right-bottom, right-top, left-bottom]
const std::array<int, 8> dirs_ = { 1, -1, nx_, -nx_, nx_ + 1, -nx_ - 1, nx_ - 1, -nx_ + 1 };
const std::unordered_map<int, std::pair<int, int>> dir_to_obs_id_ = {
{ -nx_, { 0, 1 } }, // direction bottom, obstacle detection [left-right]
{ nx_, { 0, 1 } }, // direction top, obstacle detection [left-right]
{ -1, { 2, 3 } }, // direction right, obstacle detection [top-bottom]
{ 1, { 2, 3 } }, // direction left, obstacle detection [top-bottom]
{ -nx_ - 1, { 0, 2 } }, // direction right-bottom, obstacle detection [left-top]
{ nx_ + 1, { 1, 3 } }, // direction left-top, obstacle detection [right-bottom]
{ -nx_ + 1, { 1, 2 } }, // direction left-bottom, obstacle detection [right-top]
{ nx_ - 1, { 0, 3 } }, // direction right-top, obstacle detection [left-bottom]
};
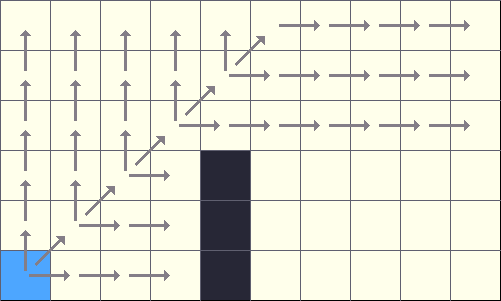
大概的坐标点分布如下图所示
通过一个一维数组来存储二维矩阵,使用 dirs_ 数组来定义 移动方向
所以 dirs_ 数组中,序号为 index 的节点,左侧节点序号是是 index + 1,上方节点序号是 index + nx_
使用 dir_to_obs_id_ 来映射 强制邻居检测
key 表示 移动方向, value 表示 dirs_ 数组的索引,用于表示检测方向
查找强制邻居
通过 dir 和 cur_id 可以确定从 哪个 方向进入的 当前节点
以上图为例,从 P 点到 X 点,方向是右移,对应的
dir_序号是 -1
- 如果是 水平移动,则需要判断新节点的 上下节点 是否存在 强制邻居
- 如果是 竖直移动,则需要判断新节点的 左右节点 是否存在 强制邻居
- 如果是 斜向移动,则需要判断新节点的 反向分解方向的节点
- 如果是 右上角移动,则需要判断新节点的 左 和 下 节点
- 如果是 左上角移动,则需要判断新节点的 右 和 下 节点
这里从 P 移动到 X 是右上角移动,则需要判断 X 的 左节点 和 下节点
bool JPSPathPlanner::_forceNeighborDetect(int dir, int cur_id, std::vector<int>& fn_id)
{
fn_id.clear();
std::array<int, 2> delta_obs = { dirs_[dir_to_obs_id_.at(dir).first], dirs_[dir_to_obs_id_.at(dir).second] };
// horizon or vertical
if (dir == 1 || dir == -1 || dir == nx_ || dir == -nx_)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
if (costmap_->getCharMap()[cur_id + delta_obs[i]] >= costmap_2d::LETHAL_OBSTACLE * obstacle_factor_ &&
costmap_->getCharMap()[cur_id + delta_obs[i] + dir] < costmap_2d::LETHAL_OBSTACLE * obstacle_factor_)
{
fn_id.push_back(cur_id + delta_obs[i] + dir);
}
}
}
// slash
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
if (costmap_->getCharMap()[cur_id + delta_obs[i]] >= costmap_2d::LETHAL_OBSTACLE * obstacle_factor_ &&
costmap_->getCharMap()[cur_id + 2 * delta_obs[i] + dir] < costmap_2d::LETHAL_OBSTACLE * obstacle_factor_)
{
fn_id.push_back(cur_id + 2 * delta_obs[i] + dir);
}
}
}
return !fn_id.empty();
}
上述情况 配和 代码,这么理解
通过 dir 从 dir_to_obs_id_ 和 dirs_ 中得到需要判断 障碍物 的方向
此时 delta_obs 的内容是 上 和 下
- 遍历
delta_obs- 如果 当前节点 的 上节点 是 障碍物,那么 当前节点 的 上节点 的 右节点 是 强制邻居
- 如果 当前节点 的 下节点 是 障碍物,那么 当前节点 的 下节点 的 右节点 是 强制邻居
注意,需要判断 强制邻居 不能是 障碍物
ostmap_->getCharMap()[id]值大于obstacle_factor_表示障碍物
上述情况 配合 代码,这么理解
通过 dir 从 dir_to_obs_id_ 和 dirs_ 中得到需要判断 障碍物 的方向
此时 delta_obs 的内容是 左 和 下
- 遍历
delta_obs- 如果 当前节点 的 左节点 是 障碍物,那么 当前节点 的 左上角 节点是 强制邻居
- 如果 当前节点 的 下节点 是 障碍物,那么 当前节点 的 右下角 节点是 强制邻居
注意,需要判断 强制邻居 不能是 障碍物
如果是斜向时,强制邻居的 id 是 cur_id + 2 * delta_obs[i] + dir,仍然以上述情况为例子
移动方向是 右上角,当前节点 的 左节点 是 障碍物,那么 当前节点 的 左上角 节点是 强制邻居
此时 delta_obs[i] 表示 左方向, cur_id + 左方向 * 2 + 右上 得到的就是 左上角
_checkStraightLine 和 _checkSlashLine
_checkStraightLine 检查所有 竖直 或者 水平 方向
_checkSlashLine 检查所有 斜向
JPS 查询一个点,是先查询这个点的斜向
比如样例代码中,先查询起点的 左上方向 和 右下方向,再查询 左下方向 和 右上方向
// initialization
for (int i = 4; i < 6; i++)
{ // explore left-top and right-bottom from current
_checkSlashLine(dirs_[i], start_, open_list_);
}
for (int i = 6; i < 8; i++)
{ // explore left-bottom and right-top from next
_checkSlashLine(dirs_[i], start_, open_list_, false);
}
在斜向查询的时候,会分解斜向向量,比如如果是 右上方向查询,会将查询区分为 右 和 上 两个方向,并一直查询下去,直到遇到 障碍物、终点、强制邻居
先查找当前点 上方向 所有点,再查询 右方向 所有点
当 当前节点 的 右方向 和 上方向 全部遍历完毕之后,沿着当前节点的 右上角 移动,再判断新节点的 右方向 和 上方向 全部节点
_jump
因为 _checkStraightLine 和 _checkSlashLine 遍历节点时,遇到 强制邻居 就会停止搜索,导致后续节点可能没有搜索完毕
通过 parent_Id 和自己的 ID,沿着未搜索完的方向继续搜索
int dir = calDir(node.id(), node.pid());
if (dir == 1 || dir == -1 || dir == nx_ || dir == -nx_)
{
_checkStraightLine(dir, node, open_list);
}
else
{
_checkSlashLine(dir, node, open_list);
}
然后沿着 强制邻居 方向继续搜索
if (node.fid() != -1)
{
int f_dir = calDir(node.fid(), node.id());
_checkSlashLine(f_dir, node, open_list, false);
}
这 _jump 函数中,仍然会向 open_list 中添加新的节点
plan
首先从 start_ 起点开始,初始化 open_list_ 的内容
// initialization
for (int i = 4; i < 6; i++)
{ // explore left-top and right-bottom from current
_checkSlashLine(dirs_[i], start_, open_list_);
}
for (int i = 6; i < 8; i++)
{ // explore left-bottom and right-top from next
_checkSlashLine(dirs_[i], start_, open_list_, false);
}
然后对 open_list_ 进行遍历,通过 _jump 对跳点进行处理
while (!open_list_.empty())
{
// pop current node from open list
auto current = open_list_.top();
open_list_.pop();
// current node do not exist in closed list
if (closed_list_.find(current.id()) != closed_list_.end())
continue;
closed_list_.insert(std::make_pair(current.id(), current));
expand.emplace_back(current.x(), current.y());
// goal found
if (current == goal_)
{
// 找到目标点
}
// 对跳点进行处理
_jump(current, open_list_);
}