|
|
пре 6 месеци | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| Image | пре 6 месеци | |
| README.md | пре 6 месеци | |
README.md
容器
TArray
虽然在 Array.h 文件中 TArray 的定义需要设置两个模板参数
template<typename InElementType, typename InAllocatorType>
class TArray
但是在日常使用时,完全不需要设置 InAllocatorType,这是因为在 ContainersFwd.h 文件中,帮助设置了默认的 InAllocatorType
template <int IndexSize> class TSizedDefaultAllocator : public TSizedHeapAllocator<IndexSize> { public: typedef TSizedHeapAllocator<IndexSize> Typedef; };
template<int IndexSize> class TSizedDefaultAllocator;
using FDefaultAllocator = TSizedDefaultAllocator<32>;
using FDefaultAllocator64 = TSizedDefaultAllocator<64>;
template<typename T, typename Allocator = FDefaultAllocator> class TArray;
template<typename T> using TArray64 = TArray<T, FDefaultAllocator64>;
所以,日常使用 TArray 的时候,默认的内存分配器就是 TSizedDefaultAllocator<32>,也就是 TSizedHeapAllocator<32>
Emplace
想要窥探 TArray 如何存储和管理对象的,从添加一个对象开始入手
template <typename... ArgsType>
FORCEINLINE SizeType Emplace(ArgsType&&... Args)
{
const SizeType Index = AddUninitialized();
new(GetData() + Index) ElementType(Forward<ArgsType>(Args)...);
return Index;
}
使用 AddUninitialized 计算内存偏移,然后再对指定空间直接 placement new 构造对象
FORCEINLINE SizeType AddUninitialized()
{
CheckInvariants();
const USizeType OldNum = (USizeType)ArrayNum;
const USizeType NewNum = OldNum + (USizeType)1;
ArrayNum = (SizeType)NewNum;
if (NewNum > (USizeType)ArrayMax)
{
ResizeGrow((SizeType)OldNum);
}
return OldNum;
}
AddUninitialized 中会判断,如果当前数量 + 1 超过了数组的最大数量,则会触发 ResizeGrow
FORCENOINLINE void ResizeGrow(SizeType OldNum)
{
SizeType LocalArrayNum = ArrayNum;
// some check ...
ArrayMax = AllocatorCalculateSlackGrow(LocalArrayNum, ArrayMax);
AllocatorResizeAllocation(OldNum, ArrayMax);
}
通过 AllocatorCalculateSlackGrow 计算了新的数组最大大小,这个函数最后调用了 Allocator 的 CalculateSlackGrow,最终会调用到 DefaultCalculateSlackGrow 这个全局函数
#if AGGRESSIVE_MEMORY_SAVING
const SIZE_T FirstGrow = 1;
#else
const SIZE_T FirstGrow = 4;
const SIZE_T ConstantGrow = 16;
#endif
#if CONTAINER_INITIAL_ALLOC_ZERO_SLACK
if (NumAllocatedElements)
{
#if AGGRESSIVE_MEMORY_SAVING
Grow = SIZE_T(NumElements) + SIZE_T(NumElements) / 4;
#else
Grow = SIZE_T(NumElements) + 3 * SIZE_T(NumElements) / 8 + ConstantGrow;
#endif
}
else if (SIZE_T(NumElements) > Grow)
{
Grow = SIZE_T(NumElements);
}
#else
if (NumAllocatedElements || SIZE_T(NumElements) > Grow)
{
#if AGGRESSIVE_MEMORY_SAVING
Grow = SIZE_T(NumElements) + SIZE_T(NumElements) / 4;
#else
Grow = SIZE_T(NumElements) + 3 * SIZE_T(NumElements) / 8 + ConstantGrow;
#endif
}
#endif
| 条件 | 内存节省模式 | 标准模式 | 设计意图 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 已分配内存 | 1.25倍扩容 Grow = N + N/4 | 1.375倍 + 常数 Grow = N + 3N/8 + 16 | 平衡内存/性能 |
| 首次分配 | 直接使用元素数 Grow = N | 1.375倍 + 常数 Grow = N + 3N/8 + 16 | 避免初始浪费 |
| 元素超限 | 直接使用元素数 Grow = N | 1.375倍 + 常数 Grow = N + 3N/8 + 16 | 安全边界处理 |
相比于 libstd++、MSVC 等的 2、1.5、1.618 扩容策略, UE 的策略相对保守
在计算完新的数组容量之后,通过 AllocatorResizeAllocation 来重设数组,最后会调用 TSizedHeapAllocator 中的 ResizeAllocation 函数
void ResizeAllocation(SizeType PreviousNumElements, SizeType NumElements, SIZE_T NumBytesPerElement)
{
if (Data || NumElements)
{
// do something ...
Data = (FScriptContainerElement*)BaseMallocType::Realloc( Data, NumElements*NumBytesPerElement );
}
}
重要的其实就一句话,那就是 BaseMallocType::Realloc 重新分配内存
RemoveAt
void RemoveAtImpl(SizeType Index, SizeType Count, bool bAllowShrinking)
{
if (Count)
{
CheckInvariants();
checkSlow((Count >= 0) & (Index >= 0) & (Index + Count <= ArrayNum));
DestructItems(GetData() + Index, Count);
SizeType NumToMove = ArrayNum - Index - Count;
if (NumToMove)
{
FMemory::Memmove
(
(uint8*)AllocatorInstance.GetAllocation() + (Index)* sizeof(ElementType),
(uint8*)AllocatorInstance.GetAllocation() + (Index + Count) * sizeof(ElementType),
NumToMove * sizeof(ElementType)
);
}
ArrayNum -= Count;
if (bAllowShrinking)
{
ResizeShrink();
}
}
}
通过地址偏移得到起始地址,通过 Count 得到需要析构的对象个数,在 DestructItems 中循环析构数组对象
然后通过 FMemory::Memmove 将删除序号后面的内容直接内存操作,补全前面的缺口
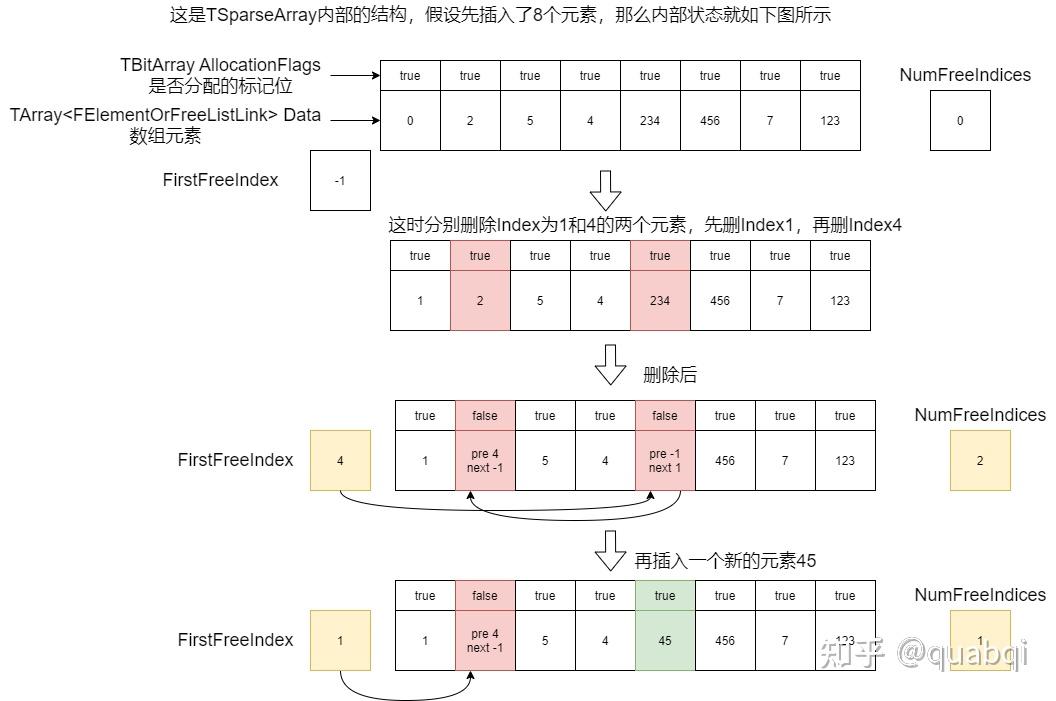
TSparseArray
template<typename InElementType,typename Allocator /*= FDefaultSparseArrayAllocator */>
class TSparseArray
TSparseArray 即 稀疏矩阵
通过定义上面的注释内容,可以窥探 TSparseArray 的作用
TSparseArray 是一个动态大小的数组,其中元素索引不一定是连续的。与普通 TArray 一样,所有内存都用于存储元素,但是支持 O(1) 时间删除元素
TSpareArray 使用 TArray 存储元素,使用 TBitArray 标记某个元素是否已经被分配
typedef TSparseArrayElementOrFreeListLink<TAlignedBytes<sizeof(ElementType), alignof(ElementType)>> FElementOrFreeListLink;
typedef TArray<FElementOrFreeListLink,typename Allocator::ElementAllocator> DataType;
DataType Data;
typedef TBitArray<typename Allocator::BitArrayAllocator> AllocationBitArrayType;
AllocationBitArrayType AllocationFlags;
/** 数组中当前包含自由元素链表第一个的未分配元素的索引 */
int32 FirstFreeIndex;
/** 空闲元素的个数 */
int32 NumFreeIndices;
正如注释所说,有一个存储数据的 TArray 数组,属性名为 Data;有一个存储序号是否空闲的 TBitArray,属性名为 AllocationFlags
FElementOrFreeListLink 存储实际内容和前后序号,这里 TAlignedBytes 用于创建一块大小和 ElementType 并且内存对齐的内存块,这样无论是蓝图对象还是C++对象都能存储,从而忽略具体类型
template<typename ElementType>
union TSparseArrayElementOrFreeListLink
{
ElementType ElementData;
struct
{
int32 PrevFreeIndex;
int32 NextFreeIndex;
};
};
其实通过 TSparseArrayElementOrFreeListLink 就可以知道 TSparseArray 怎么实现的了
使用 FirstFreeIndex 记录空闲元素链表的入口;使用 NumFreeIndices 记录空闲元素个数,方便一些操作的条件判断
RemoveAt
void RemoveAt(int32 Index,int32 Count = 1)
{
if (!TIsTriviallyDestructible<ElementType>::Value)
{
FElementOrFreeListLink* DataPtr = (FElementOrFreeListLink*)Data.GetData();
for (int32 It = Index, ItCount = Count; ItCount; ++It, --ItCount)
{
((ElementType&)DataPtr[It].ElementData).~ElementType();
}
}
RemoveAtUninitialized(Index, Count);
}
删除指定序号上的对象
操作也很简单,通过 Index 获取 Data 中的对象,并对其调用析构函数
然后调用 RemoveAtUninitialized 更新 空闲元素链表信息
void RemoveAtUninitialized(int32 Index,int32 Count = 1)
{
FElementOrFreeListLink* DataPtr = (FElementOrFreeListLink*)Data.GetData();
for (; Count; --Count)
{
check(AllocationFlags[Index]);
// Mark the element as free and add it to the free element list.
if(NumFreeIndices)
{
DataPtr[FirstFreeIndex].PrevFreeIndex = Index;
}
DataPtr[Index].PrevFreeIndex = -1;
DataPtr[Index].NextFreeIndex = NumFreeIndices > 0 ? FirstFreeIndex : INDEX_NONE;
FirstFreeIndex = Index;
++NumFreeIndices;
AllocationFlags[Index] = false;
++Index;
}
}
通过 Data.GetData() 配合 Index 获取指定的数组元素
修改结构体中 PrevFreeIndex 和 NextFreeIndex 指向的空闲元素序号
设置 AllocationFlags,将对应元素序号标记为 false,也就是空闲
Add
int32 Add(const ElementType& Element)
{
FSparseArrayAllocationInfo Allocation = AddUninitialized();
new(Allocation) ElementType(Element);
return Allocation.Index;
}
通过 AddUninitialized 获取对应的内存地址,然后就地 placement new 来构建对象
AddUninitialized 有两种情况
NumFreeIndices不为 0,表示存在空闲元素,通过FirstFreeIndex获取空闲元素,修改空闲元素链表关系
FElementOrFreeListLink* DataPtr = (FElementOrFreeListLink*)Data.GetData();
Index = FirstFreeIndex;
FirstFreeIndex = DataPtr[FirstFreeIndex].NextFreeIndex;
--NumFreeIndices;
if(NumFreeIndices)
{
DataPtr[FirstFreeIndex].PrevFreeIndex = -1;
}
NumFreeIndices为 0,表示不存在空闲元素,需要扩容Data数组和AllocationFlags标记数组
Index = Data.AddUninitialized(1);
AllocationFlags.Add(false);
至于为什么能对 Allocation 执行 placement new 操作,这是因为实现对应的 operator new
inline void* operator new(size_t Size,const FSparseArrayAllocationInfo& Allocation)
{
UE_ASSUME(Allocation.Pointer);
return Allocation.Pointer;
}
TSet
template<
typename InElementType,
typename KeyFuncs /*= DefaultKeyFuncs<ElementType>*/,
typename Allocator /*= FDefaultSetAllocator*/
>
class TSet
TSet 定义如上,与 TArray 类似,在使用 TSet 时需要定义 KeyFuncs 和 Allocator,不过为什么可以直接使用 TSet<AActor> 呢?
依然是 ContainersFwd.h 文件中,预先定义好了一些东西
template<typename InElementType, typename KeyFuncs = DefaultKeyFuncs<InElementType>, typename Allocator = FDefaultSetAllocator> class TSet;
TSet 中也是维护一个容器,用于存储对象。这个容器就是名为 Elements,它的类型是 TSparseArray
TSparseArray前面有做解释
using ElementArrayType = TSparseArray<SetElementType, typename Allocator::SparseArrayAllocator>;
using HashType = typename Allocator::HashAllocator::template ForElementType<FSetElementId>;
ElementArrayType Elements;
Emplace
与 TArray 类似,参考添加一个节点,了解内存结构
template <typename ArgsType = ElementType>
FSetElementId Emplace(ArgsType&& Args, bool* bIsAlreadyInSetPtr = nullptr)
{
// Create a new element.
FSparseArrayAllocationInfo ElementAllocation = Elements.AddUninitialized();
SetElementType& Element = *new (ElementAllocation) SetElementType(Forward<ArgsType>(Args));
SizeType NewHashIndex = ElementAllocation.Index;
uint32 KeyHash = KeyFuncs::GetKeyHash(KeyFuncs::GetSetKey(Element.Value));
if (!TryReplaceExisting(KeyHash, Element, NewHashIndex, bIsAlreadyInSetPtr))
{
RehashOrLink(KeyHash, Element, NewHashIndex);
}
return FSetElementId(NewHashIndex);
}
在 Emplace 函数中,从 Elements 中获取一个内存块,对其调用 placement new ,并且对值进行 Hash 计算