|
|
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
|
|
* @Autor: LC
|
|
|
* @Date: 2022-01-20 10:45:55
|
|
|
* @LastEditors: Please set LastEditors
|
|
|
- * @LastEditTime: 2022-02-05 01:38:42
|
|
|
+ * @LastEditTime: 2022-02-05 16:52:27
|
|
|
* @Description: file content
|
|
|
-->
|
|
|
# JavaScipt语法
|
|
|
@@ -3041,4 +3041,328 @@ Promise.any([p1, p2, p3]).then(res => {
|
|
|
// resolve 1
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
-##
|
|
|
+## 迭代器生成器 (iterator - generator)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### 迭代器
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 生成器可以处理异步代码
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+**迭代器**可以使用户在容器对象上遍历对象,使用该接口无需关心对象的内部实现细节
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+`JavaScript`中,迭代器也是一个**具体对象**,这个对象需要符合**迭代器协议**
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 迭代器协议定义了产生一系列值的标准方式,在js中就是实现特定的`next`*方法*
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- `next`方法有一些要求
|
|
|
+ - 无参或一个参数的函数,返回一个应当拥有以下两个属性的对象
|
|
|
+ - `done`(**boolean**)
|
|
|
+ - 如果迭代器可以产生序列中的下一个值,则为false
|
|
|
+ - 如果容器已经被迭代完毕,则为true
|
|
|
+ - `value`:该值可选,如果`done = true`,则value作为迭代结束后默认返回值
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 当所有元素**都访问完**了,最后再访问的时候`done = true`,其他时候`done = false`
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+// 迭代器对象基本形状
|
|
|
+// const iterator = {
|
|
|
+// next : function(){
|
|
|
+// return {
|
|
|
+// done : true,
|
|
|
+// value : 123
|
|
|
+// }
|
|
|
+// }
|
|
|
+// };
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+const names = ["q", "w", "e", "r"];
|
|
|
+let index = 0;
|
|
|
+const namesIterator = {
|
|
|
+ next : function() {
|
|
|
+ if(index < names.length){
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ done : false,
|
|
|
+ value : names[index++]
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ else{
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ done : true,
|
|
|
+ value : undefined
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+console.log(namesIterator.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(namesIterator.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(namesIterator.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(namesIterator.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(namesIterator.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(namesIterator.next());
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+// 输出
|
|
|
+// { done: false, value: 'q' }
|
|
|
+// { done: false, value: 'w' }
|
|
|
+// { done: false, value: 'e' }
|
|
|
+// { done: false, value: 'r' }
|
|
|
+// { done: true, value: undefined }
|
|
|
+// { done: true, value: undefined }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+function createArrayIterator(arr){
|
|
|
+ let index = 0;
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ next : function(){
|
|
|
+ if(index < arr.length){
|
|
|
+ return { done : false, value : arr[index++]};
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ else{
|
|
|
+ return { done : true, value : undefined};
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+#### 可迭代对象
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+[Symbol.iterator](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Symbol/iterator)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+const iteratorObj = {
|
|
|
+ names: ["q", "w", "e"],
|
|
|
+ [Symbol.iterator]: function() {
|
|
|
+ let index = 0;
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ next: () => { // 匿名函数
|
|
|
+ if (index < this.names.length) {
|
|
|
+ return { done: false, value: this.names[index++] };
|
|
|
+ } else {
|
|
|
+ return { done: true, value: undefined };
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+const iterator = iteratorObj[Symbol.iterator]();
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator.next());
|
|
|
+const iterator1 = iteratorObj[Symbol.iterator]();
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator1.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator1.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator1.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator1.next());
|
|
|
+const iterator2 = iteratorObj[Symbol.iterator]();
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator2.next());
|
|
|
+console.log(iterator2.next());
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+for (let item of iteratorObj) {
|
|
|
+ console.log(item);
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+// 错误例子
|
|
|
+const errorObj = {
|
|
|
+ names: ["q", "w", "e"],
|
|
|
+ [Symbol.iterator]: function() {
|
|
|
+ let index = 0;
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ next: function() { // 匿名函数
|
|
|
+ if (index < this.names.length) {
|
|
|
+ return { done: false, value: this.names[index++] };
|
|
|
+ } else {
|
|
|
+ return { done: true, value: undefined };
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+for (let item of errorObj) {
|
|
|
+ console.log(item);
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+1. 注意`[Symbol.iterator]`中的`next`使用的是**箭头函数**,如果`next`绑定的是`function`,那么`this`指向的就是`[Symbol.iterator]`**返回的对象**,而不是`iteratorObj`对象,而只有`iteratorObj`对象才有`names`属性
|
|
|
+2. 当使用**箭头函数**时,不绑定`this`,而是使用上层作用域作为`this`,而上层作用域就是`iteratorObj`
|
|
|
+3. 在错误示例中,`this`指向的是`{next: function() {if (index < this.names.length) {return { done: false, value: this.names[index++] };} else {return { done: true, value: undefined };}}`对象
|
|
|
+4. `for...of...`通过迭代器判断返回值的`done`是否为`true`来决定是否停止遍历
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+#### 原生迭代器对象
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+平时创建的很多原生对象已经实现了可迭代协议,会生成一个迭代器对象:String、Array、Map、Set、arguments对象、NodeList集合
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+const names = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
|
|
|
+console.log(names[Symbol.iterator]);
|
|
|
+console.log(names[Symbol.iterator]().next());
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+const set = new Set();
|
|
|
+set.add(1);
|
|
|
+set.add(2);
|
|
|
+set.add(3);
|
|
|
+console.log(set[Symbol.iterator]);
|
|
|
+console.log(set[Symbol.iterator]().next());
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+#### 可迭代对象的应用
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+1. Javascript语法中:`for...of...`、展开语法(Spread syntax)、yield*、解构赋值(Destructuring assignment)
|
|
|
+2. 创建按一些对象时:`new Map([Iterable])`、`new WeakMap([iterable])`、`new Set([iterable])`、`new WeakSet([iterable])`
|
|
|
+3. 一些方法调用:`Promise.all(iterable)`、`Promise.race(iterable)`、`Array.from(ietrable)`
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+const iteratorObj = {
|
|
|
+ names: ["q", "w", "e"],
|
|
|
+ [Symbol.iterator]: function() {
|
|
|
+ let index = 0;
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ next: () => { // 匿名函数
|
|
|
+ if (index < this.names.length) {
|
|
|
+ return { done: false, value: this.names[index++] };
|
|
|
+ } else {
|
|
|
+ return { done: true, value: undefined };
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+// 展开语法
|
|
|
+const indexs = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
|
|
|
+const newIndexs = [...indexs, ...iteratorObj];
|
|
|
+console.log(newIndexs); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'q', 'w', 'e']
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+// 结构语法
|
|
|
+const [index1, index2, index3] = iteratorObj;
|
|
|
+console.log(index1, index2, index3); // ['q', 'w', 'e']
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+// 创建一些对象
|
|
|
+const set = new Set(iteratorObj); // 可以通过可迭代对象创建Set
|
|
|
+console.log(set); // Set(3) { 'q', 'w', 'e' }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+const array = Array.from(iteratorObj);
|
|
|
+console.log(array); // [ 'q', 'w', 'e' ]
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+#### 自定义类的可迭代
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- 教室案例
|
|
|
+ - 教室的名称、位置、学生
|
|
|
+ - 可以进入新学生
|
|
|
+ - 可迭代对象
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+class ClassRoom {
|
|
|
+ constructor(address, name, students) {
|
|
|
+ this.address = address;
|
|
|
+ this.name = name;
|
|
|
+ this.students = students;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ entry(newStudent) {
|
|
|
+ this.students.push(newStudent);
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ [Symbol.iterator]() {
|
|
|
+ let index = 0;
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ next: () => {
|
|
|
+ if (index < this.students.length) {
|
|
|
+ return { done: false, value: this.students[index++] };
|
|
|
+ } else {
|
|
|
+ return { done: true, value: undefined };
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ },
|
|
|
+ // 监听迭代器终止
|
|
|
+ return : () => {
|
|
|
+ console.log("迭代器终止");
|
|
|
+ return { done : true, value : undefined };
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+const c1 = new ClassRoom("", "", [1, 2, 3]);
|
|
|
+for (let s of c1) {
|
|
|
+ console.log(s);
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+for (let s of c1) {
|
|
|
+ if (s == 2) {
|
|
|
+ break;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ console.log(s);
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 可以通过添加`return`属性监听迭代器的迭代终止,**注意返回值**
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### 生成器
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 比较特殊的迭代器
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ES6中新增的一种函数控制、使用的方方案,它可以让我们更加灵活的控制函数什么时候继续执行、暂停执行
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> return 虽然可以暂停函数执行,但后续代码无法继续执行
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+**生成器对象是由生成器函数产生的**
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- 生成器函数也是一个函数,但是和普通函数有一些区别
|
|
|
+ - 生成器函数需要在`function`的后面加一个符号:`*`
|
|
|
+ - 生成器函数可以通过`yield`关键字来控制函数的执行流程
|
|
|
+ - 生成器函数的返回值是一个`Generator`(生成器)
|
|
|
+ - 生成器事实上是一种特殊的迭代器
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
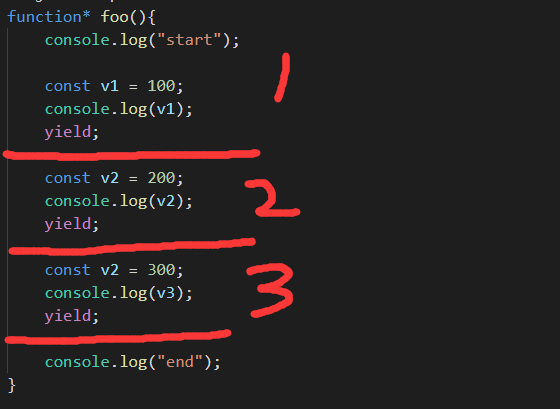
+function* foo() {
|
|
|
+ console.log("start");
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ const v1 = 100;
|
|
|
+ console.log(v1);
|
|
|
+ const n1 = yield v1;
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ const v2 = 200;
|
|
|
+ console.log(v2, n1);
|
|
|
+ const n2 = yield v2;
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ const v3 = 300;
|
|
|
+ console.log(v3, n2);
|
|
|
+ const n3 = yield v3;
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ console.log("end", n3);
|
|
|
+ return "123";
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+foo(); // 直接执行foo,不会执行任何代码
|
|
|
+const generator = foo();
|
|
|
+console.log("---------");
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+// 开始执行第一段代码 看下图
|
|
|
+console.log("---------", generator.next(666));
|
|
|
+// 开始执行第二段代码
|
|
|
+console.log("---------", generator.next(777));
|
|
|
+// 开始执行第三段代码
|
|
|
+console.log("---------", generator.next(888));
|
|
|
+// 开始执行第四段代码
|
|
|
+console.log("---------", generator.next(999));
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+// 运行结果
|
|
|
+// ---------
|
|
|
+// start
|
|
|
+// 100
|
|
|
+// --------- { value: 100, done: false }
|
|
|
+// 200 777
|
|
|
+// --------- { value: 200, done: false }
|
|
|
+// 300 888
|
|
|
+// --------- { value: 300, done: false }
|
|
|
+// end 999
|
|
|
+// --------- { value: '123', done: true }
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+生成器函数以`yiled`为分界线,分段执行
|
|
|
+通过上述代码的`next`的返回值可见,返回值的结构与**迭代器**的`next`结构相同,可见**生成器**就是特殊的**迭代器**
|
|
|
+当生成器函数遇到`yield`的时候停止执行,`done`的值为`false`;当生成器函数遇到`return`的时候,`done`的值就变成`true`了
|
|
|
+`yield v1;`表示返回生成器的值为`v1`的值
|
|
|
+`const n1 = yield v1;`表示用`n1`接受`next`传入参数的值
|