|
|
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
|
|
* @Autor: LC
|
|
|
* @Date: 2022-01-20 10:45:55
|
|
|
* @LastEditors: LC
|
|
|
- * @LastEditTime: 2022-01-24 18:34:56
|
|
|
+ * @LastEditTime: 2022-01-25 16:36:53
|
|
|
* @Description: file content
|
|
|
-->
|
|
|
# JavaScipt语法
|
|
|
@@ -264,7 +264,7 @@ JS引用使用标记清除算法,V8引擎为了更好的优化,它在算法
|
|
|
|
|
|
**JS中函数是一等公民**,函数可以作为参数传递、作为返回值
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function foo(func){
|
|
|
func();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
@@ -300,7 +300,7 @@ fn();
|
|
|
- 闭包能让你可以在一个内层函数中访问到其外层函数的作用域
|
|
|
- 在JS中,每当创建一个函数,闭包就会在函数创建的同时被创建出来
|
|
|
|
|
|
- ```js
|
|
|
+ ```javascript
|
|
|
function run(){
|
|
|
var name = "run";
|
|
|
function rush(){
|
|
|
@@ -321,7 +321,7 @@ fn();
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-## apply、call、bind
|
|
|
+### apply、call、bind
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -335,7 +335,7 @@ fn();
|
|
|
> **副作用**:在**执行一个函数**时,除了**返回函数值**以外,对**调函数产生了附加的影响**,比如修**改了全局变量**、**修改参数或者改变外部的存储**
|
|
|
> 副作用往往是**产生BUG的温床**
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var names = ["avc", "cba", "eax", "fas"];
|
|
|
// 纯函数,确定输入确定输出,没有副作用(没有修改外部变量等,原来的数组name没有被修改)
|
|
|
var name2 = names.slice(0, 3);
|
|
|
@@ -367,7 +367,7 @@ function foo2(num1, num2) { // 非纯函数 修改了外界的值
|
|
|
- 柯里化生成**如果你固定某些参数,你将得到接受余下参数的一个函数**
|
|
|
- 只**传递给函数一部分参数来调用它,让它返回一个函数去处理剩余的参数**
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function foo(m, n, x, y){
|
|
|
return m + n * 2 + x * 3 + y * y;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
@@ -405,7 +405,7 @@ var bar2 = m => n => x => y => {
|
|
|
- 让代码可以复用
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
// 柯里化的代码复用
|
|
|
|
|
|
function MakeAddr(num){
|
|
|
@@ -431,7 +431,7 @@ Add(5, 3); // 5 + 3
|
|
|
|
|
|
> 如果需要频繁对一个数进行加减处理,使用柯里化的代码比普通写法的字母数更少(不用每次都写"5,")
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
// 函数的形参个数
|
|
|
function adddd(x, y, z){
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -464,7 +464,7 @@ function hyCurring(fn){
|
|
|
- 那么可以将两个函数组合起来,**自动依次调用**
|
|
|
- 这个**对函数的组合过程**称之为**组合函数**
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function double(num){
|
|
|
return num * 2;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
@@ -512,7 +512,7 @@ function hyCompose(...fns){
|
|
|
|
|
|
### JS其他函数知识
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var message = "VO : GO";
|
|
|
var obj = {name : "Y", message = "Obj message"};
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -531,7 +531,7 @@ foo(); // 输出 Obj message
|
|
|
> `with() {}`语句用于定义对象查找作用域
|
|
|
> 不建议使用with语句,存在兼容性问题
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var jsString = 'var message = "hello world"; console.log(message);'
|
|
|
eval(jsString;)
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@@ -557,7 +557,7 @@ eval(jsString;)
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 创建对象
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
// 创建对象 方式1 使用Object类和new关键字来创建对象
|
|
|
var obj2 = new Object();
|
|
|
obj.name = "y";
|
|
|
@@ -579,7 +579,7 @@ var obj = {
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 操作对象属性
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {
|
|
|
name : "y",
|
|
|
age : 16
|
|
|
@@ -598,7 +598,7 @@ for (var key in obj){ // 遍历属性
|
|
|
|
|
|
为了对属性进行比较精准的操作控制,我们可以使用**属性描述符**,通过属性描述符**可以精准的添加或修改对象的属性**,属性描述符需要使用`Object.defineProperty`来对属性进行添加或修改
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
// obj : 对象、prop : 属性、descriptor : 属性描述符
|
|
|
Object.defineProperty(obj, prop, descriptor);
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@@ -639,7 +639,7 @@ Object.defineProperty(obj, prop, descriptor);
|
|
|
> 对于不需要进行额外处理的数据可以使用**数据属性描述符**,比如`PI = 3.1415926`
|
|
|
> 对于需要额外处理的数据,比如年龄只能是10~20就需要使用**存取属性描述符**
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {
|
|
|
name : "y",
|
|
|
age : 16
|
|
|
@@ -656,7 +656,7 @@ console.log(obj);
|
|
|
|
|
|
> 这里obj并不会输出height属性,因为`height`是通过属性描述符添加的所以`enumerable`默认为false
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
// configurable展示
|
|
|
// obj就是前面的obj
|
|
|
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'height', {
|
|
|
@@ -676,7 +676,7 @@ Object.defineProperty(obj, 'height', {
|
|
|
console.log(obj.height); // 180 没有被修改成200,因为configurable最开始是false
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
// enumerable展示
|
|
|
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'height', {
|
|
|
value : 180,
|
|
|
@@ -687,7 +687,7 @@ console.log(obj); // 此时可以正常打印出height属性
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {
|
|
|
name : "y",
|
|
|
age : 16 ,
|
|
|
@@ -711,7 +711,7 @@ Object.defineProperty(obj, 'address', {
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 定义多个属性描述符
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {
|
|
|
_age : 0,
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
@@ -738,7 +738,7 @@ console.log(obj);
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 另一种使用get/set的方法
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {
|
|
|
_age : 10,
|
|
|
set age(value){
|
|
|
@@ -754,7 +754,7 @@ console.log(obj);
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 获得对应属性的属性描述符
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {
|
|
|
_age: 0,
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
@@ -763,7 +763,7 @@ console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, "_age"));
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 获得对象的所有属性描述符
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {
|
|
|
name: "y",
|
|
|
age: 16,
|
|
|
@@ -776,19 +776,19 @@ console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj));
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 禁止对象继续添加新的属性
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
Object.preventExtensions(obj);
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 禁止对象配置/删除属性
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
Object.seal(obj);
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 让对象属性变成不可修改(writable : false)
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
Object.freeze(obj);
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
@@ -798,7 +798,7 @@ Object.freeze(obj);
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. 工厂方法创建对象
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function createPerson(name, age){
|
|
|
var person{};
|
|
|
person.name = name;
|
|
|
@@ -813,7 +813,7 @@ var p3 = createPerson("name3", 12);
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. 构造函数:创建对象时会调用的函数
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function foo(){
|
|
|
console.log("hello world");
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
@@ -832,7 +832,7 @@ console.log(f2); // 返回了一个foo类型的对象
|
|
|
4. 执行函数的内部代码(函数体代码)
|
|
|
5. 如果构造函数没有返回非空对象,则返回创建出来的新对象
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function Person(name, age, height){
|
|
|
this.name = name;
|
|
|
this.age = age;
|
|
|
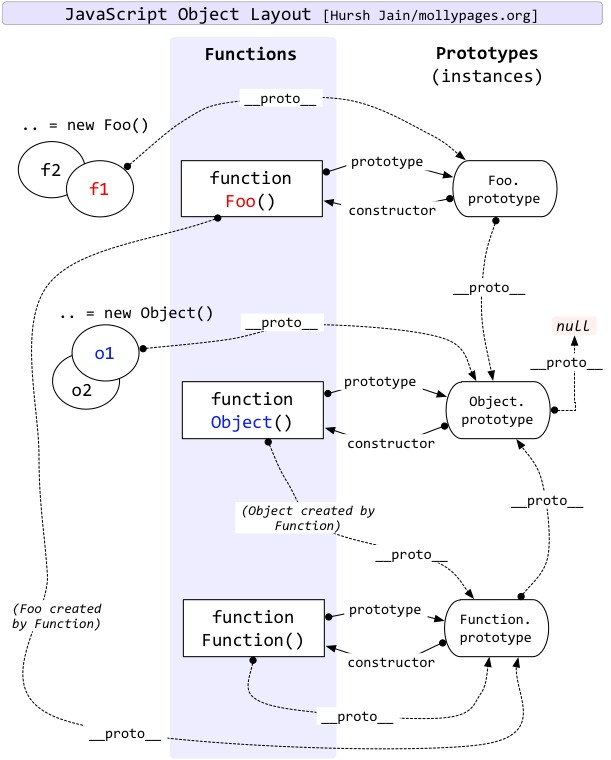
@@ -864,7 +864,7 @@ JavaScript当中每个对象都有一个特殊的内置属性`[[prototype]]`,
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 原型的作用
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {};
|
|
|
obj.__proto__.age = 10;
|
|
|
console.log(obj.age);
|
|
|
@@ -884,7 +884,7 @@ console.log(obj.age);
|
|
|
> `[[prototype]]`和`prototype`不是一个东西,前者是理论名称,后者是实际属性
|
|
|
> `fun.__proto__`中的`__proto__`并不是标准支持的,而是部分浏览器为了方便程序员debug而增加的
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function Person() {
|
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
@@ -906,7 +906,7 @@ console.log(p1.name, " ", p2.name);
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
foo.prototype = {
|
|
|
name : "y",
|
|
|
age : 19,
|
|
|
@@ -925,7 +925,7 @@ Object.defineProperty(foo.prototype, "constructor", {
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 原型与构造函数结合
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function Person(name, age){
|
|
|
this.name = name;
|
|
|
this.age = age;
|
|
|
@@ -943,7 +943,7 @@ p2.eating();
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 原型链和继承
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function Person(name, age){
|
|
|
this.name = name;
|
|
|
this.age = age;
|
|
|
@@ -960,7 +960,7 @@ var p2 = new Person("y", 10);
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 原型链
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {
|
|
|
name : "y"
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
@@ -970,18 +970,18 @@ console.log(obj.address);
|
|
|
|
|
|
`obj`对象并没有`address`属性,所以回去`obj.__proto__`原型上查找,如果也没有就会在`obj.__proto__.__proto__`上去查找直到找到或者顶层原型为止,这种**类似链表**的查找方式就是**原型链**
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
|
|
|
> 顶层`__proto__`就是`Object.__proto__`
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
var obj = {};
|
|
|
console.log(obj.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // true
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function Person(name, age){
|
|
|
this.name = name;
|
|
|
this.age = age;
|
|
|
@@ -1028,7 +1028,7 @@ s1.studying();
|
|
|
- 因此通过`apply()`或`call()`方法也可以在新创建的对象上执行构造函数
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-```js
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
function Person(name, age, friends){
|
|
|
this.name = name;
|
|
|
this.age = age;
|
|
|
@@ -1064,3 +1064,369 @@ var s1 = new Student("y", 10, ["1", "2"], 1);
|
|
|
|
|
|
一种继承方法,不是通过构造函数实现的方法
|
|
|
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+var obj = {
|
|
|
+ name : "y",
|
|
|
+ age : 16
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+function createObject(protoObj){
|
|
|
+ var newObj = {};
|
|
|
+ Object.setPrototypeOf(newObj, protoObj); // 设置newObj的原型为protoObj
|
|
|
+ return newObj;
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+// 不适用Object函数库实现设置原型的方法
|
|
|
+function createObject2(protoObj){
|
|
|
+ function Fn() {}
|
|
|
+ Fn.prototype = protoObj;
|
|
|
+ var new Obj = new Fn();
|
|
|
+ return newObj;
|
|
|
+ // newObj.__proto__ = protoObj; // 不可这么写,因为__proto__不是所有js引擎都支持
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+// 创建info对象的原型指向obj对象
|
|
|
+var info = {};
|
|
|
+console.log(info);
|
|
|
+console.log(info.__proto__);
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+info = Object.create(obj); // 功能等价于 createObject 和 createObject2
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> `Object.setPrototypeOf(newObj, protoObj);`设置newObj的原型为protoObj
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+#### 寄生式继承
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+**寄生式继承**的思路是结合**原型类继承**和**工厂模式**的一种方式
|
|
|
+即创建一个封装继承过程的函数,该函数在内部以某种方式来增强对象,最后再将这个对象返回
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+var personObj = {
|
|
|
+ running = function() {
|
|
|
+ console.log("running");
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+function createStudent(person, name){ // 工厂函数
|
|
|
+ var stu = Object.create(person); // 原型式继承
|
|
|
+ stu.name = name;
|
|
|
+ stu.studying = function() {
|
|
|
+ console.log("studying");
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+var stu1 = createStudent(person, "x");
|
|
|
+var stu2 = createStudent(person, "y");
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 每个对象的`studying()`方法都是新建的
|
|
|
+> `stu1`和`stu2`没有明确的类型(consolo.log一下就知道)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+#### 寄生组合式继承(最终方案)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+function CreateObject(o){
|
|
|
+ function Fn (){}
|
|
|
+ Fn.prototype = o;
|
|
|
+ return new Fn;
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+function Person(name, age, friends){
|
|
|
+ this.name = name;
|
|
|
+ this.age = age;
|
|
|
+ this.friends = friends;
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Person.prototype.running = function() {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this.name + " running");
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+function Student(name, age, friends, sno, score) {
|
|
|
+ Person.call(this, name, age, friends);
|
|
|
+ this.sno = sno;
|
|
|
+ this.score = score;
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Student.prototype = CreateObject(Person.prototype);
|
|
|
+Student.prototype.studying = function() {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this.name + " studying " + this.score);
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+var stu = new Student("x", 10, [], 1, 100);
|
|
|
+console.log(stu); //Person { name: 'x', age: 10, friends: [], sno: 1, score: 100 }
|
|
|
+stu.running(); // x running
|
|
|
+stu.studying(); // x studying 100
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 输出`stu`是`Person`类的,因为输出的是`constructor`的`name`属性,而这里的`constructor`使用的是`Person`的所以最后输出的名字是`Person`
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+function inheritPrototype(SubType, SuperType){
|
|
|
+ SubType.prototype = CreateObject(SuperType.prototype);
|
|
|
+ Object.defineProperty(SubType.prototype, 'constructor', {
|
|
|
+ enumerable : false,
|
|
|
+ configurable : true,
|
|
|
+ writable : true,
|
|
|
+ value : SubType
|
|
|
+ });
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+inheritPrototype(Student, Person);
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 手动设置`Student`的`constructor`是`Student`自己就行了
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### 原型判断方法补充
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+var obj = {
|
|
|
+ name : "w",
|
|
|
+ age : 19
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+var info = Object.create(obj, {
|
|
|
+ address : {
|
|
|
+ value : "BJ",
|
|
|
+ enumerable : true
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+});
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+console.log(info);
|
|
|
+console.log(info.hasOwnProperty('address')); // true
|
|
|
+console.log(info.hasOwnProperty('name')); // false
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+console.log("address" in info); // true
|
|
|
+console.log("name" in info); // true
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 创建对象时,为新对象添加属性描述符
|
|
|
+> `info.hasOwnProperty('address')`判断属性是否是自己的属性
|
|
|
+> `"name" in info`判断对象是否存在name属性
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+------
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+`instanceof`用于检测构造函数的`prototype`是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+function CreateObject(o){
|
|
|
+ function Fn (){}
|
|
|
+ Fn.prototype = o;
|
|
|
+ return new Fn;
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+function inheritPrototype(SubType, SuperType){
|
|
|
+ SubType.prototype = CreateObject(SuperType.prototype);
|
|
|
+ Object.defineProperty(SubType.prototype, 'constructor', {
|
|
|
+ enumerable : false,
|
|
|
+ configurable : true,
|
|
|
+ writable : true,
|
|
|
+ value : SubType
|
|
|
+ });
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+function Person(){
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+function Student() {
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+inheritPrototype(Student, Person);
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+var stu = new Student()
|
|
|
+console.log(stu instanceof Student); // true
|
|
|
+console.log(stu instanceof Person); // true
|
|
|
+console.log(stu instanceof Object); // true
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> `instanceof`后面的必须是构造函数
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### 原型的继承关系
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+JavaScript当中每个对象都有一个特殊的内置属性`[[prototype]]`,这个特殊的对象可以指向另一个对象,一般把`[[prototype]]`称为隐式原型(一般看不到、不会改、用不到)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+var obj = {};
|
|
|
+console.log(obj.__proto__);
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+函数是一个**对象**,所以也有隐式原型`[[prototype]]`
|
|
|
+函数存在一个显示原型`prototype`
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+当创建一个函数后,JS引擎会自动给函数对象添加属性`Foo.prototype = { constructor : Foo }`
|
|
|
+定义`Foo()`函数时,相当于`new Funtion()`创建函数对象,这时编译器执行`Foo.__proto__ = Function.prototype`,而`Function.prototype = { constructor : Function } `
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> `Function`是极为特殊的对象,它的`prototype`和`__proto__`相等
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+function Foo(){
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+console.log(Foo.__proto__);
|
|
|
+console.log(Foo.prototype);
|
|
|
+console.log(Foo.prototype === Foo.__proto__); // false
|
|
|
+console.log(Foo.prototype.constructor); // Function : Foo
|
|
|
+console.log(Foo.__proto__.constructor); // Function : Function
|
|
|
+console.log(Function.prototype === Function.__proto__); // true
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+## ES6~ES12
|
|
|
+### JS面向对象(ES6及后续版本,前面是旧版JS的创建对象,比较复杂)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 理论上 `class` 的底层实现方式还是 **上述的旧版创建代码**
|
|
|
+> 使用**babel**可以将代码装成旧版本代码
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+1. 每一个类都有自己的构造函数(方法),这个方法的名称固定为`constructor`
|
|
|
+2. 通过new操作符,操作一个类的时候会调用类的`constructor`方法
|
|
|
+3. 每个类只能有一个`constructor`方法,如果有多个会抛出异常
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+// 类声明
|
|
|
+class Person{
|
|
|
+ constructor(name, age){
|
|
|
+ this.name = name;
|
|
|
+ this.age = age;
|
|
|
+ this._address = "";
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ eating() {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this.name + " eating");
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ running() {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this.name + " running");
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ // 访问器
|
|
|
+ get address(){
|
|
|
+ return this._address;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ set address(value){
|
|
|
+ this._address = value;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ // 静态方法
|
|
|
+ static createPerson(){
|
|
|
+ return new Person("", 1);
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+console.log(Person.prototype);
|
|
|
+console.log(Person.prototype.constructor); // 指向当前Person
|
|
|
+console.log(typeof Person); // function
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+// 类的表达式 用的比较少
|
|
|
+var Animal = class {
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+var p1 = new Person("x", 1);
|
|
|
+var p2 = new Person("y", 2);
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- 类的继承
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+`super`关键字,一般用在三个地方:子类的构造函数、实例方法、静态方法
|
|
|
+在**子类的构造函数**中使用this或者返回默认对象之前,必须先通过`super`调用**父类的构造函数**
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+class Person{
|
|
|
+ constructor(name, age){
|
|
|
+ this.name = name;
|
|
|
+ this.age = age;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ eating() {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this.name + " eating");
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+class Student extends Person {
|
|
|
+ constructor(name, age, sno){
|
|
|
+ super(name, age); // 调用父类构造方法
|
|
|
+ // super.eating(); // 调用父类的方法
|
|
|
+ this.sno = sno;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ // 方法的重写
|
|
|
+ eating() {
|
|
|
+ console.log("Student " + this.name + " eating");
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+};
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+-----
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- 使用`babel`转换ES6为ES5
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+[在线babel网站](https://babeljs.io/)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### 继承内置类
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+class MyArray extends Array{
|
|
|
+ firstItem(){
|
|
|
+ return this[0];
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ lastItem(){
|
|
|
+ return this[this.length-1];
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+var arr = new MyArray(1, 2, 3);
|
|
|
+console.log(arr.firstItem());
|
|
|
+console.log(arr.lastItem());
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 扩展数组功能
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### 类的混入 mixin
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Javascirpt的类只支持单继承,也就是说它只能有一个父类
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```javascript
|
|
|
+class Person{
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+class Runner {
|
|
|
+ running(){
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+class Eater {
|
|
|
+ eating() {
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+function mixinRunner(BaseClass){
|
|
|
+ class NewClass extends BaseClass {
|
|
|
+ running() {
|
|
|
+ console.log("running");
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ return NewClass;
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+class Student extends Person{
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+var NewStudent = mixinRunner(Student);
|
|
|
+var ns = new NewStudent();
|
|
|
+ns.running();
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 通过`mixinRunner`扩展类的功能
|
|
|
+
|