|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,358 @@
|
|
|
+# Vue.js
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+## 简单使用
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 介绍、例子
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+`Vue` 的本质就是一个 `Javascript` 的库
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+使用方式
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+1. 页面中通过 `CDN` 导入
|
|
|
+2. 下载 `Vue` 的 `JS` 文件
|
|
|
+3. 通过 `npm` 包管理工具安装
|
|
|
+4. 直接通过 `Vue CLI` 工具生成项目
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+以当前官网推荐的 `CDN` 地址为例,从源码上看可以发现 `VueJS` 定义了一个全局变量 `Vue`,很多功能都是直接通过这个全局对象进行操控的
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+以直接通过 `CDN` 导入为例
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```html
|
|
|
+<!DOCTYPE html>
|
|
|
+<html lang="en">
|
|
|
+<head>
|
|
|
+ <meta charset="UTF-8">
|
|
|
+ <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
|
|
|
+ <title>My Web Page</title>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+</head>
|
|
|
+<body>
|
|
|
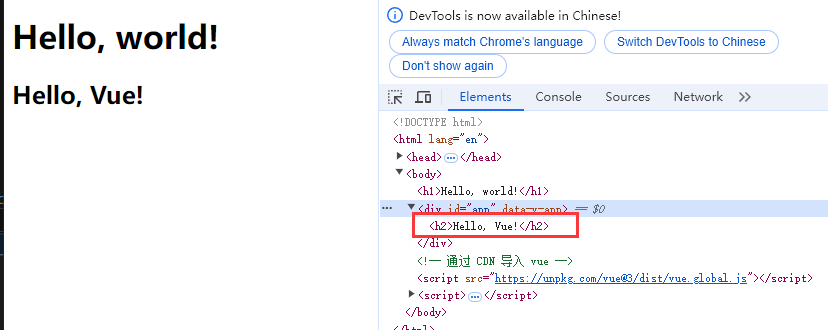
+ <h1>Hello, world!</h1>
|
|
|
+ <div id="app"> </div>
|
|
|
+ <!-- 通过 CDN 导入 vue -->
|
|
|
+ <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script>
|
|
|
+ <script>
|
|
|
+ const app = Vue.createApp({
|
|
|
+ template: `<h2>{{ message }}</h2>`,
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ data() {
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ message: 'Hello, Vue!'
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ });
|
|
|
+ app.mount('#app'); // 将 App 对象挂载到 id 为 app 的元素上
|
|
|
+ </script>
|
|
|
+</body>
|
|
|
+</html>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+通过 `Vue.createApp` 创建了一个 `Vue` 对象,再通过 `id` 将对象绑定到 `<div id="app">` 中
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> `mount` 就是挂载
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```html
|
|
|
+<script>
|
|
|
+Vue.createApp({
|
|
|
+ template: `
|
|
|
+ <h2> value = {{ counter }}</h2>
|
|
|
+ <button @click='increment'>+1</button>
|
|
|
+ <button @click='decrement'>-1</button>
|
|
|
+ `,
|
|
|
+ // 定义属性,data 是个函数
|
|
|
+ data: function() {
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ counter: 100
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ },
|
|
|
+ // 定义方法
|
|
|
+ methods: {
|
|
|
+ increment() {
|
|
|
+ this.counter++;
|
|
|
+ },
|
|
|
+ decrement() {
|
|
|
+ this.counter--;
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+}).mount("#app1");
|
|
|
+</script>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+使用响应式,Vue 中使用 `{{ }}` 可以获取 `data` 返回的对象中的属性,在 `methods` 中可以通过 `this` 获取 `data` 返回对象的**代理**
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+对比原生的 JS 和 Vue 的开发来说
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- 原生 JS 更像命令式编程,即先获取对象,再修改参数,最后设置回去
|
|
|
+- Vue 更像是声明式编程,即提前声明数据、方法,然后将数据和方法绑定到 `template` 中,将显示与数据进行分离
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+通常将 Vue 看作是 MVVM(Module-Vie-MoudleView) 框架。虽然官方说法是 Vue 并没有完全遵守 MVVM 模型,但整体设计受 MVVM 的启发
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+如上图所示
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+- 通常将 `Dom` 或者 `Vue` 对象中的 `template` 认为是 `View`(视图)
|
|
|
+ - 因为 `Vue` 的 `template` 会先生成 `vdom` 再渲染为真实 `Dom`
|
|
|
+- 通常将整个 Javascript 对象看作是 Module
|
|
|
+ - 一般 `Vue` 对象的 `template` 会分离出去,保留 `data` 和 `methods`,这一块被认为是 `Module`
|
|
|
+- `Vue` 帮助将 `Module` 和 `View` 进行绑定,比如 `View` 直接通过 `{{message}}` 就可以显示 `Module` 的 `data` 的 `message` 属性
|
|
|
+ - 按上图,`Vue` 进行了 `Data Bindings` 进行数据绑定,将 Model 的数据绑定到 View 上
|
|
|
+ - 按上图,`Vue` 进行了 `Dom Listeners` 进行了事件监听
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### template、data、methods
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+通过前面的例子,已经可以知道 `Vue.createApp` 传入对象的 `template` 属性的作用了,Vue 通过 `template` 属性进行一个效果显示
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+`template` 属性就表示 `Vue` 需要帮助渲染的模板信息。其中会写很多 Html 标签,这些标签会替换掉关在到的元素的 innerHTML
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+`template` 中有一些起卦的语法,比如 `{{}}`、`@click`,这些都是 `template` 特有的语法
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> 也就说如果原本挂载标签中有内容,Vue 挂载之后会先把原内容清空
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+不过这个 `template` 的写法略显麻烦,并且 IDE 无法提供提示
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+因此 Vue 提供了两种来解决这个问题
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+1. 使用 script 标签,并且标记类型为 x-template
|
|
|
+2. 使用任意标签(通常使用 template,因为不会被渲染),设置 id
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> template 元素是一种用于保存客户端内容的机制,该内容在加载页面时不会被呈现,但随后在运行时使用 JS 实例化
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```html
|
|
|
+<script type="x-template" id="template1">
|
|
|
+ <h2>{{ message }}</h2>
|
|
|
+</script>
|
|
|
+<div id="app2"></div>
|
|
|
+<script>
|
|
|
+ Vue.createApp({
|
|
|
+ // 通过 template1 查找 id 为 template1 的标签并将内容设置到 template 中
|
|
|
+ template: '#template1',
|
|
|
+ data() {
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ message: 'Hello, Vue!'
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }).mount('#app2');
|
|
|
+</script>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```html
|
|
|
+<div id="app3"></div>
|
|
|
+<template id="template2">
|
|
|
+ <h2>{{ message }}</h2>
|
|
|
+</template>
|
|
|
+<script>
|
|
|
+ Vue.createApp({
|
|
|
+ template: '#template2',
|
|
|
+ data() {
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ message: 'Hello, Vue! template2'
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }).mount('#app3');
|
|
|
+</script>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> [template标签](https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTML/Element/template)
|
|
|
+> 其实不仅可以用 template,还可以使用其他任何标签,主要是 template 不会被渲染。因为本质来说都是使用 `document.querySelector` 来查找对象
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+------------------------
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+通过前面的例子,可以知道传入 `Vue.createApp` 的对象的 `data` 属性的作用,该属性在 Vue3 中必须是一个函数,否则**报错**
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+data 中返回的对象会被 Vue 的响应式系统劫持,只会对该对象的修改或者访问都会在劫持中被处理
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+这就是为什么 `{{message}}` 可以显示 `message` 的数据,以及为什么修改 `message` 的值其显示内容也会改变
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+------------------------
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+通过前面的例子,可以知道传入 `Vue.createApp` 的对象的 `methods` 属性用于定义系列功能函数,这些方法可以绑定到 `template` 模板中,同时这些方法可以通过 `this` 关键字来直接访问到 `data` 中返回的对象的属性
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+-----------------------
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+除了前面几个属性之外,还有可以定义很多其他的属性,比如:`props`、`computed`、`watch`、`emits`、`setup` 和 **声明周期函数**等
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### 源码查看
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+[Github仓库](https://github.com/vuejs/core)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+在 `dev` 中开启 `sourcemap` 源码映射,然后示例项目进行测试即可
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### methods 中禁止使用箭头函数
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```html
|
|
|
+<div id="app3"></div>
|
|
|
+<template id="template2">
|
|
|
+ <h2>{{ message }}</h2>
|
|
|
+ <button @click="btnClick">测试</button>
|
|
|
+</template>
|
|
|
+<script>
|
|
|
+ Vue.createApp({
|
|
|
+ template: '#template2',
|
|
|
+ data() {
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ message: 'Hello, Vue! template2'
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ },
|
|
|
+ methods: {
|
|
|
+ btnClick: () => {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this);
|
|
|
+ console.log(this.message);
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }).mount('#app3');
|
|
|
+</script>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+首先 `methods` 中定义的函数通常要通过 `this` 来访问 `data` 的属性,如果 `methods` 里面定义箭头函数,函数中使用的 `this` 其实是 `Window` 对象,也就是浏览器窗口对象
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+在 `Window` 对象中肯定是没有名为 `message` 的属性的,所以使用 `this.message` 会直接报错
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+在箭头函数中是不绑定 `this` 的
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```html
|
|
|
+<script>
|
|
|
+ const foo = function() {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this);
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ foo(); // 输出 Window
|
|
|
+ const obj = {bar: foo};
|
|
|
+ obj.bar(); // 输出 obj 对象
|
|
|
+</script>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+普通函数执行时都会进行 `this` 的绑定,也就是说 `foo()` 其实是 `Window.foo()` 进行了隐式绑定
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```html
|
|
|
+<script>
|
|
|
+ const foo = () => {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this);
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ foo(); // 输出 Window
|
|
|
+ const obj = {bar: foo};
|
|
|
+ obj.bar(); // 输出 Window
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ const foo1 = foo.bind(obj);
|
|
|
+ foo1();
|
|
|
+</script>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+箭头函数不会绑定 `this`,所以此时无论是 `foo()` 还是 `obj.bar()` 输出的都是 `Window`
|
|
|
+为什么都是都是 `Window` 是因为箭头函数中的 this 并没有进行任何绑定,所以找不到 `this` 对象,于是就会像上层作用域查找 `this` 对象,最后找到 `Window` 对象
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```html
|
|
|
+<script>
|
|
|
+ const obj = {
|
|
|
+ {
|
|
|
+ template: '#template2',
|
|
|
+ data() {
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ message: 'Hello, Vue! template2'
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ },
|
|
|
+ methods: {
|
|
|
+ btnClick: () => {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this);
|
|
|
+ console.log(this.message);
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ Vue.createApp(obj).mount('#app3');
|
|
|
+</script>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+这里 `btnClick` 的上层作用域并不是 `methods`,`methods` 只是在定义对象,`obj` 也只是定义对象,所以 `btnClick` 上层作用域其实是 `<script>` 最终找的的是 `Window`
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+[this的绑定规则](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg5MDAzNzkwNA==&mid=2247483847&idx=1&sn=fe8089ded81098b35461d3c14bb85cde)
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+以源码 `componentOptions.ts` 中代码示例
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```ts
|
|
|
+if (methods) {
|
|
|
+ for (const key in methods) {
|
|
|
+ const methodHandler = (methods as MethodOptions)[key]
|
|
|
+ if (isFunction(methodHandler)) {
|
|
|
+ // In dev mode, we use the `createRenderContext` function to define
|
|
|
+ // methods to the proxy target, and those are read-only but
|
|
|
+ // reconfigurable, so it needs to be redefined here
|
|
|
+ if (__DEV__) {
|
|
|
+ Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
|
|
|
+ value: methodHandler.bind(publicThis),
|
|
|
+ configurable: true,
|
|
|
+ enumerable: true,
|
|
|
+ writable: true,
|
|
|
+ })
|
|
|
+ } else {
|
|
|
+ ctx[key] = methodHandler.bind(publicThis)
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ if (__DEV__) {
|
|
|
+ checkDuplicateProperties!(OptionTypes.METHODS, key)
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ } else if (__DEV__) {
|
|
|
+ warn(
|
|
|
+ `Method "${key}" has type "${typeof methodHandler}" in the component definition. ` +
|
|
|
+ `Did you reference the function correctly?`,
|
|
|
+ )
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+> `const publicThis = instance.proxy`
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+通过上述代码,可以看到其实就是将 `methods` 中每个函数都取出来然后通过 `bind` 绑定函数的 `this` 为 `publicThis`
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+关于 `bind` 的使用,当一个方法使用 `bind` 绑定对象时会返回一个新的方法,新的方法就是绑定了对象之后的方法
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```js
|
|
|
+function foo() {
|
|
|
+ console.log(this);
|
|
|
+}
|
|
|
+foo(); // 输出 Window
|
|
|
+var obj = {bar: "foo"};
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+var foo1 = foo.bind(obj);
|
|
|
+foo1();
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+### 模板语法
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+React 使用的 jsx,对应的代码都是编写的类似于 js 的一种语法。之后通过 Babel 将 jsx 编译成 React.CreateElement 函数调用
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+Vue 也支持 Jsx 的开发模式,但是大多数情况系啊,使用基于 HTML 的模板语法。在模板中,允许开发者以声明式的方式将 **DOM** 和 **底层组件实例的数据** 绑定在一起。在底层的实现中, VUe 将模板编译成虚拟 DOM 渲染函数
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+如果希望将数据显示到模板中,使用最多的语法是 `Mustache` 语法(双大括号)的文本插值,`Mustache` 不仅支持属性显示还支持 JS 表达式和函数调用
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+```html
|
|
|
+<div id="app4"></div>
|
|
|
+<template id="template3">
|
|
|
+ <h2>{{ getReverseMessage() }}</h2>
|
|
|
+ <h2>{{ message }}</h2>
|
|
|
+ <h2>{{ `${message} ~~~~~~~~~` }}</h2>
|
|
|
+ <h2>{{ message.split(" ") }}</h2>
|
|
|
+ <h2>{{ message === undefined ? "true" : "false" }}</h2>
|
|
|
+</template>
|
|
|
+<script>
|
|
|
+ Vue.createApp({
|
|
|
+ template: '#template3',
|
|
|
+ data() {
|
|
|
+ return {
|
|
|
+ message: 'Hello Vue! template2'
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ },
|
|
|
+ methods: {
|
|
|
+ getReverseMessage() {
|
|
|
+ return this.message.split(" ").reverse().join(" ");
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }
|
|
|
+ }).mount('#app4');
|
|
|
+</script>
|
|
|
+```
|
|
|
+
|