54 измењених фајлова са 324 додато и 0 уклоњено
+ 0
- 0
CMake/.gitignore → 构建项目/CMake/.gitignore
+ 0
- 0
CMake/Image/001.png → 构建项目/CMake/Image/001.png
+ 0
- 0
CMake/Image/002.png → 构建项目/CMake/Image/002.png
+ 0
- 0
CMake/Image/003.png → 构建项目/CMake/Image/003.png
+ 0
- 0
CMake/Image/004.png → 构建项目/CMake/Image/004.png
+ 0
- 0
CMake/Image/005.png → 构建项目/CMake/Image/005.png
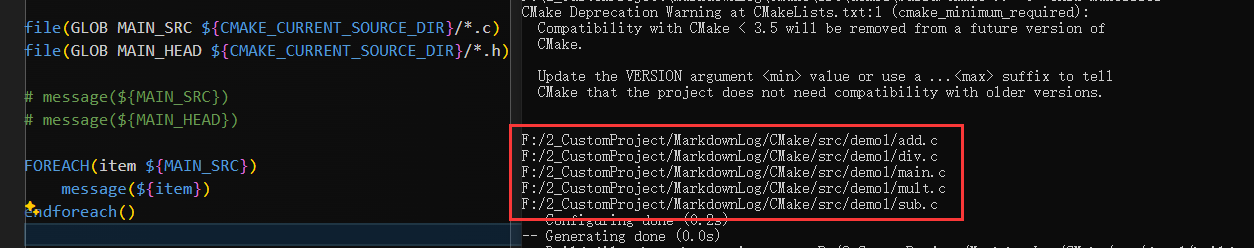
+ 0
- 0
CMake/Image/006.png → 构建项目/CMake/Image/006.png
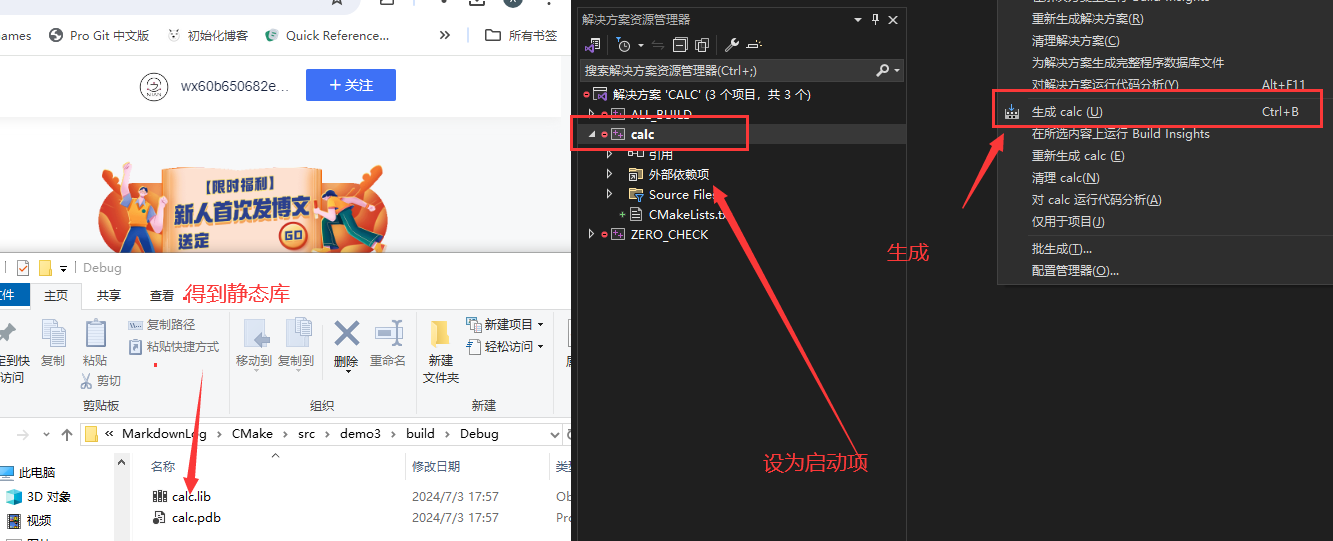
+ 0
- 0
CMake/Image/007.png → 构建项目/CMake/Image/007.png

+ 0
- 0
CMake/Image/008.png → 构建项目/CMake/Image/008.png
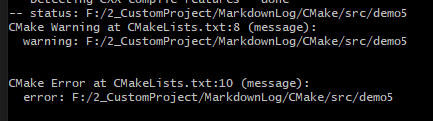
+ 0
- 0
CMake/README.md → 构建项目/CMake/README.md
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo1/CMakeLists.txt → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo1/CMakeLists.txt
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo1/add.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo1/add.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo1/div.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo1/div.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo1/head.h → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo1/head.h
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo1/main.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo1/main.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo1/mult.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo1/mult.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo1/sub.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo1/sub.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo2/CMakeLists.txt → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo2/CMakeLists.txt
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo2/include/head.h → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo2/include/head.h
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo2/src/add.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo2/src/add.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo2/src/div.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo2/src/div.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo2/src/main.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo2/src/main.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo2/src/mult.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo2/src/mult.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo2/src/sub.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo2/src/sub.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo3/CMakeLists.txt → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo3/CMakeLists.txt
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo3/include/head.h → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo3/include/head.h
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo3/src/add.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo3/src/add.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo3/src/div.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo3/src/div.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo3/src/main.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo3/src/main.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo3/src/mult.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo3/src/mult.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo3/src/sub.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo3/src/sub.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo4/CMakeLists.txt → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo4/CMakeLists.txt
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo4/include/head.h → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo4/include/head.h
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo4/src/add.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo4/src/add.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo4/src/div.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo4/src/div.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo4/src/main.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo4/src/main.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo4/src/mult.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo4/src/mult.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo4/src/sub.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo4/src/sub.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo5/CMakeLists.txt → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo5/CMakeLists.txt
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo5/include/head.h → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo5/include/head.h
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo5/src/add.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo5/src/add.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo5/src/div.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo5/src/div.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo5/src/main.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo5/src/main.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo5/src/mult.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo5/src/mult.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo5/src/sub.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo5/src/sub.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo6/CMakeLists.txt → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo6/CMakeLists.txt
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo6/include/head.h → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo6/include/head.h
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo6/src/main.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo6/src/main.c
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo7/CMakeLists.txt → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo7/CMakeLists.txt
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo7/include/head.h → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo7/include/head.h
+ 0
- 0
CMake/src/demo7/src/main.c → 构建项目/CMake/src/demo7/src/main.c
+ 0
- 0
构建项目/GN/.gitignore
+ 320
- 0
构建项目/GN/README.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 4
- 0
构建项目/README.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||